|
1Institute
for Geophysics and Planetary
Physics, University of California,
San Diego, CA, USA 2University
of Texas Institute for Geophysics,
Austin, TX, USA We compile Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2 repeat
acquisitions surrounding the time of the
2021 earthquake and use GMTSAR software to
process the raw data. Interferograms are
Gaussian filtered at 200 m and re-sampled at
50 m before further processing. We unwrap
the phase using the Statistical-Cost,
Network-Flow Algorithm for Phase Unwrapping
(SNAPHU), with nearest neighbor
interpolation over the low coherence areas
and water surfaces. The resulting LOS plots
below show surface deformation in the
line-of-sight of the observing satellite,
where positive indicates that the ground
pixel has moved towards the satellite. Download a Google Earth project file
containing all InSAR pairs included below as
layers. Also includes features picked from
these pairs and other published resources to
contextualize the InSAR data. Most
recent Google Earth project KMZ files
LOS data are available for download below. They are provided as csv files, are downsampled to 500m, and have the following columns:
lon, lat, elevation (m), look vector (E), look vector (N), look vector (U), los (mm) *Note: look vectors point from the specified point on the ground towards the observing satellite. *Note: earthquake-spanning Sentinel pairs may not capture the full extent of coseismic deformation but are included for completeness. For more information, see https://doi.org/10.1785/0120220109 <SAT>_<PATH>_<DATE1>-<DATE2>_<DATATYPE>_<DTR>.<EXT> SAT = Satellite (ALOS-2 is A2, Sentinel is S1) PATH = A or D indicates ascending or descending pass, followed by the track/path number. DATE1 = Primary scene acquisition in the format YYYYMMDD DATE2 = Reference scene acquisition in the format YYYYMMDD DATATYPE = LOS in this case DTR = will include “_dtr” if the dataset has been detrended by removing a simple ramp. EXT = LOS data files are in .csv format Click
here to download all CSV files Available files include: Co & postseismic & secondary fault
structures Descending coseismic interferogram Ascending coseismic interferogram
Mw7.2 Nippes, Haiti
Earthquake:
Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2
Interferometry
H.
Zoe Yin1, Xioahua
Xu2, Jennifer
S. Haase1, Roby
Douilly3, David
T. Sandwell1,
Bernard
Mercier de Lépinay4
3University
of California, Riverside, CA,
USA
4
CNRS Université
Côte d'Azur, Valbonne, France


The Mw7.2
Nippes, Haiti earthquake struck on August
14, 2021 (8:29 am local time)
on Haiti's southwest peninsula.
The earthquake occurred 125 km west of
Port-au-Prince at a depth of 10 km with an
oblique thrust faulting mechanism. The
earthquake occurred along the
Enriquillo-Plantain Garden fault (EPGF) zone,
about 100 km west of the Mw7.0
2010 Haiti earthquake.
Two InSAR satellites were operational before the
earthquake and continue to collect measurements
of line-of-sight (LOS) deformation. The C-band
Sentinel-1 satellites, operated by the European
Space Agency (ESA), provide a 6-day
coverage (ascending and descending tracks) of
the earthquake sequence. These data are
available on the Sentinel Data Hub. The
L-band ALOS-2 satellite, operated by the
Japanese Aerospace Exploration Agency (JAXA),
collected ascending ScanSAR data can be found on
the
ALOS-2 User Interface Gateway.
This page is to provide line-of-sight
deformation data from Sentinel-1 and ALOS-2
surrounding the 2021 earthquake. The InSAR data
are processed with open source software GMTSAR
and mapped using Generic Mapping Tools (GMT).
The InSAR phase are filtered
with a 300 m Gaussian filter and the
line-of-sight data are acquired by merging
different swaths' phase and then unwrapped using
snaphu. We also include KMZ
files for visualization in Google Earth with
some interpretations.
A manuscript published in Bulletin of the
Seismological Society of America based this
data is available here: https://doi.org/10.1785/0120220109
Background
Data
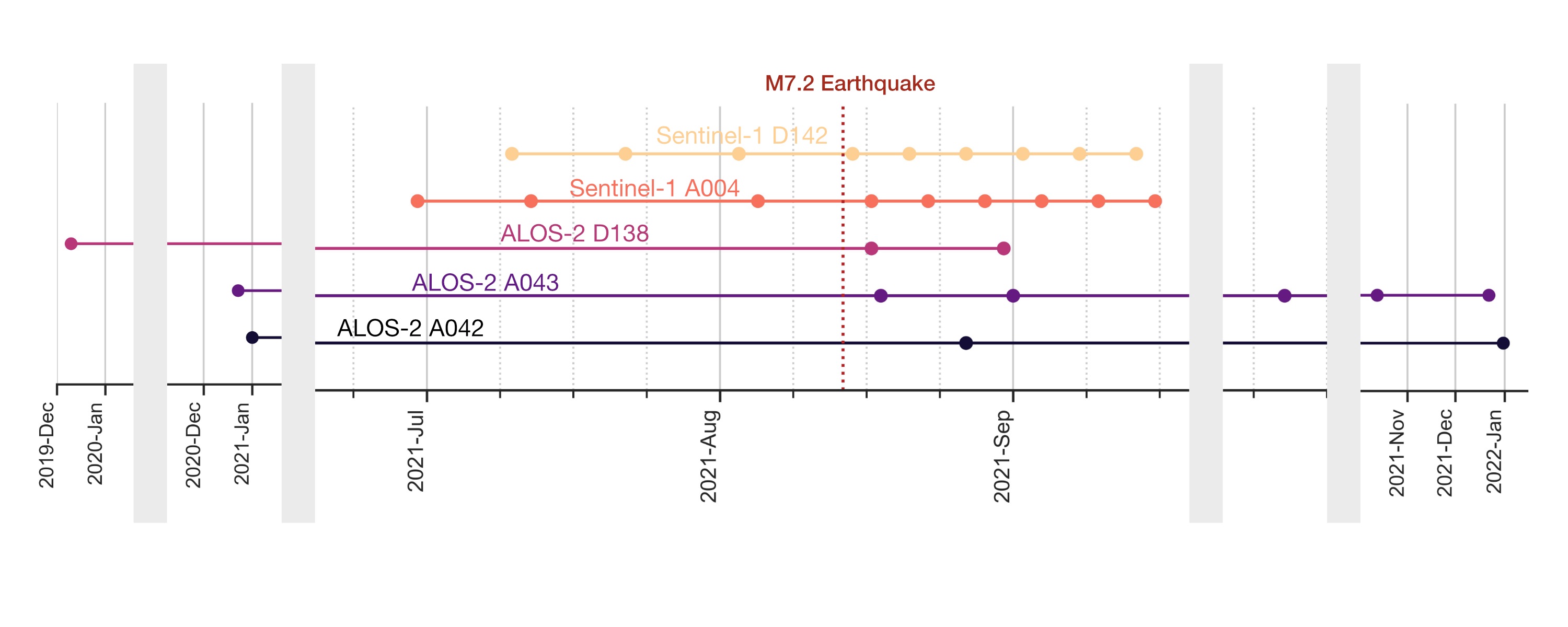
Timeline of all SAR
scene acquisitions used in this work
with the vertical red dashed line
marking the Aug 14 earthquake.
Sentinel-1 acquisitions are
frequent, with ascending and
descending acquisitions less than
two weeks before the 2021
earthquake. In contrast, ALOS-2
acquisitions are infrequent with the
closest usable ALOS-2 acquisitions
prior to the earthquake are more
than 6 months before the earthquake.
Note the breaks in the horizontal
axis in grey which represent large
time periods between ALOS-2
acquisitions.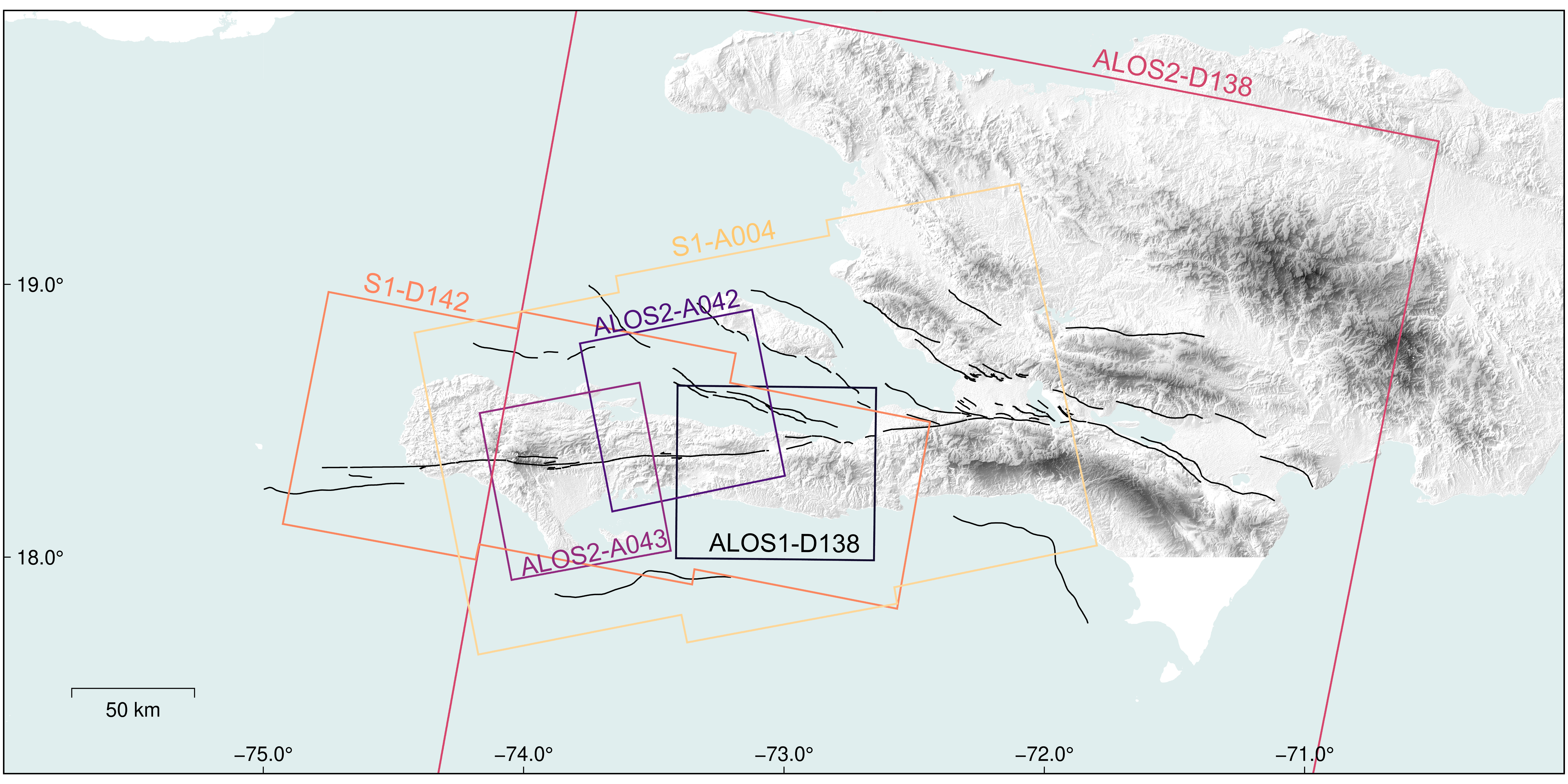
All InSAR scene outlines, note the
addition of the ALOS-1 scene which was
acquired following the 2010 earthquake.
Google Earth Project Download
Line of Sight (LOS) vectors for modeling
File names are in the format:
A2_A042_20210101-20210827_los.csv
A2_A042_20210101-20210827_los_dtr.csv
A2_A042_20210827-20211231_los.csv
A2_A042_20210827-20211231_los_dtr.csv
A2_A043_20201223-20210818_los.csv
A2_A043_20210818-20210901_los.csv
A2_D138_2019-12-10_2021-08-17_los.csv
A2_D138_20191210-20210817_los.csv
A2_D138_20191210-20210817_los_dtr.csv
A2_D144_20210819_20210902_los.csv
S1_A004_20210805-20210817_p06_80_los.csv
S1_A004_20210817-20210823_los.csv
S1_A004_20210823-20210829_dtr_los.csv
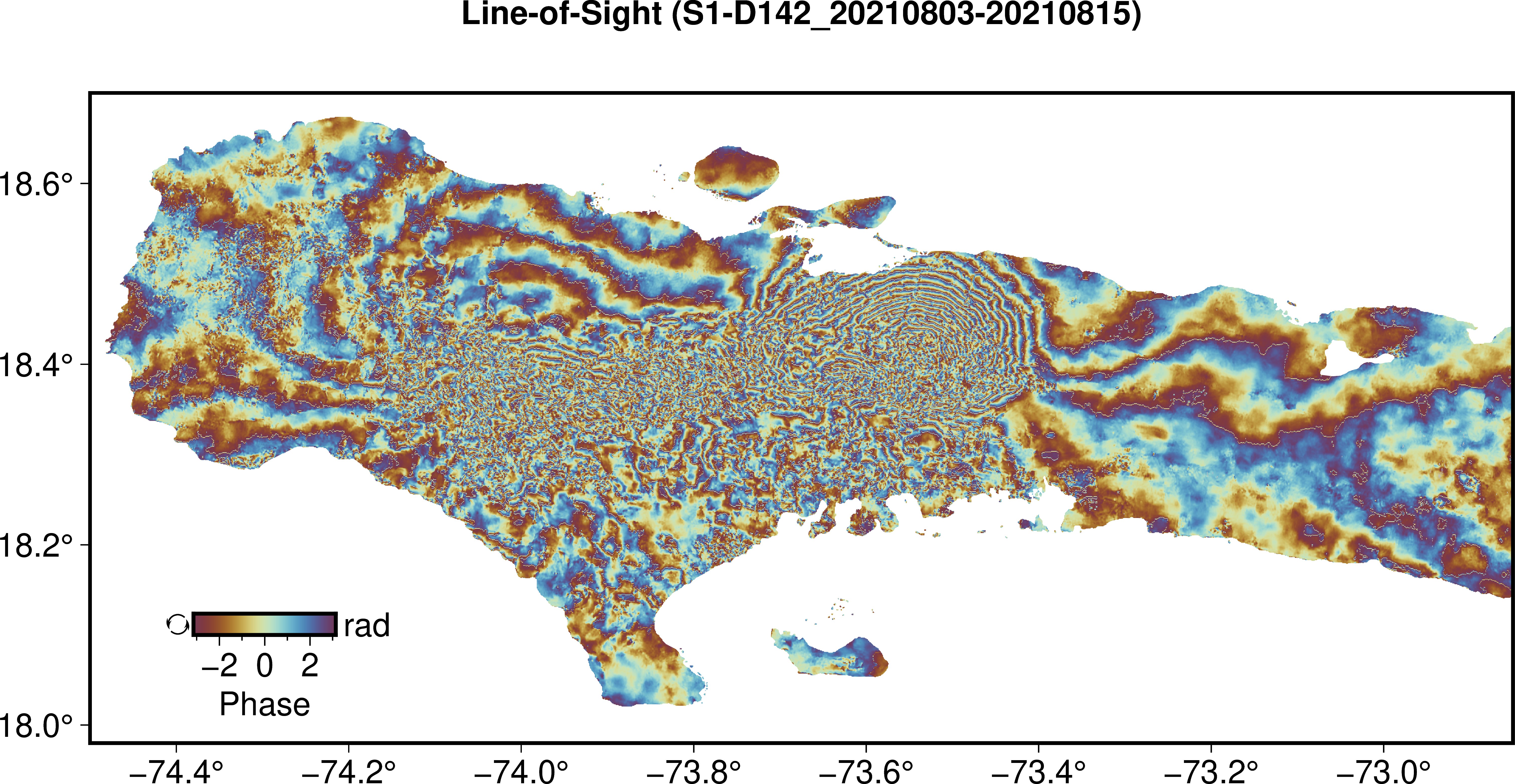
S1_D142_20210803-20210815_los.csv
S1_D142_20210803-20210815_los_dtr.csv
S1_D142_20210821-20210827_los.csv
S1_D142_20210821-20210827_los_dtr.csv
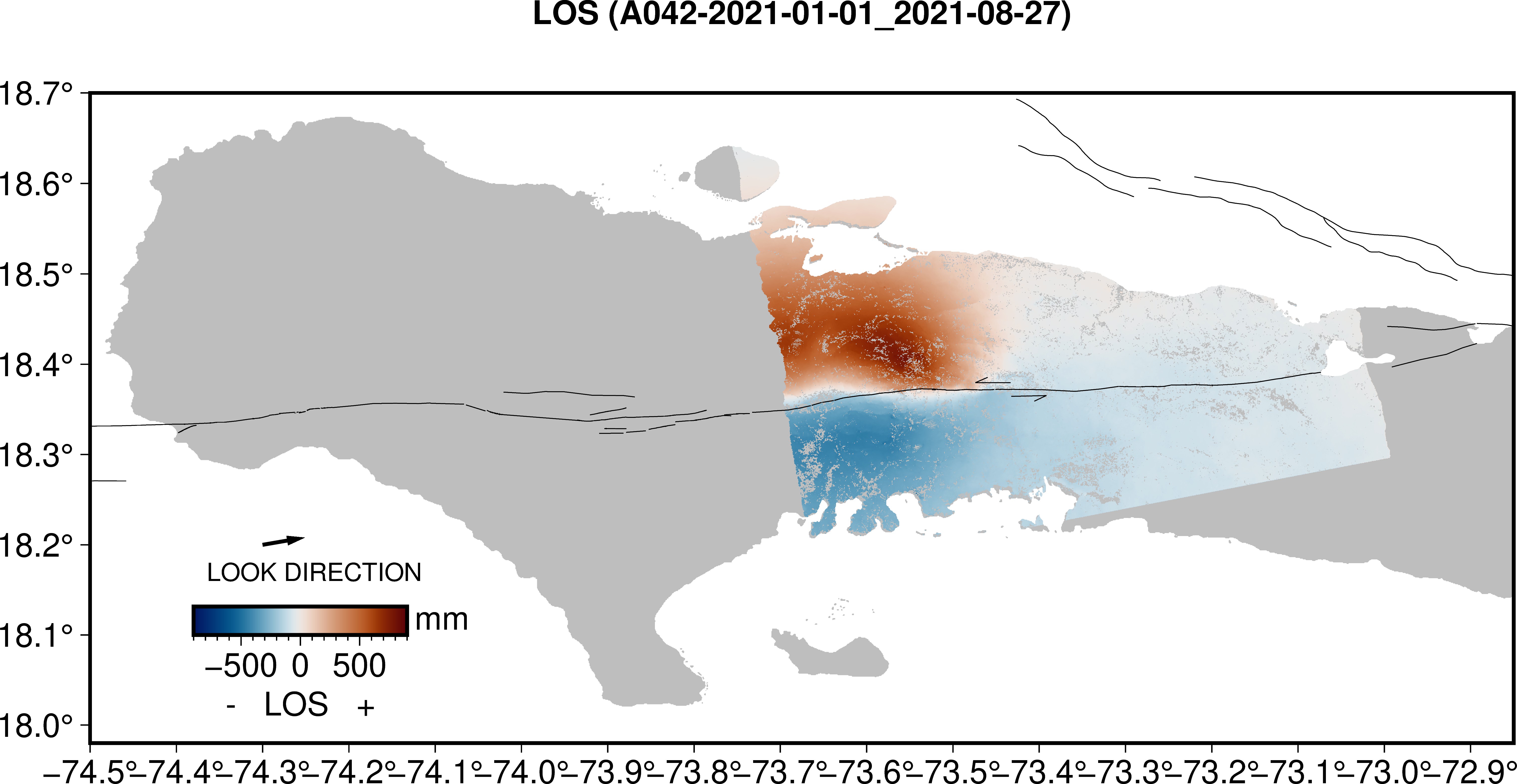
ALOS-2 Ascending Track 042 (Stripmap): Pair
2021/01/01 - 2021/08/27
PHASE: phasefilt_ll.grd
PHASE
GRADIENT: yphase_mask_ll.grd
LINE OF SIGHT: los_ll.grd
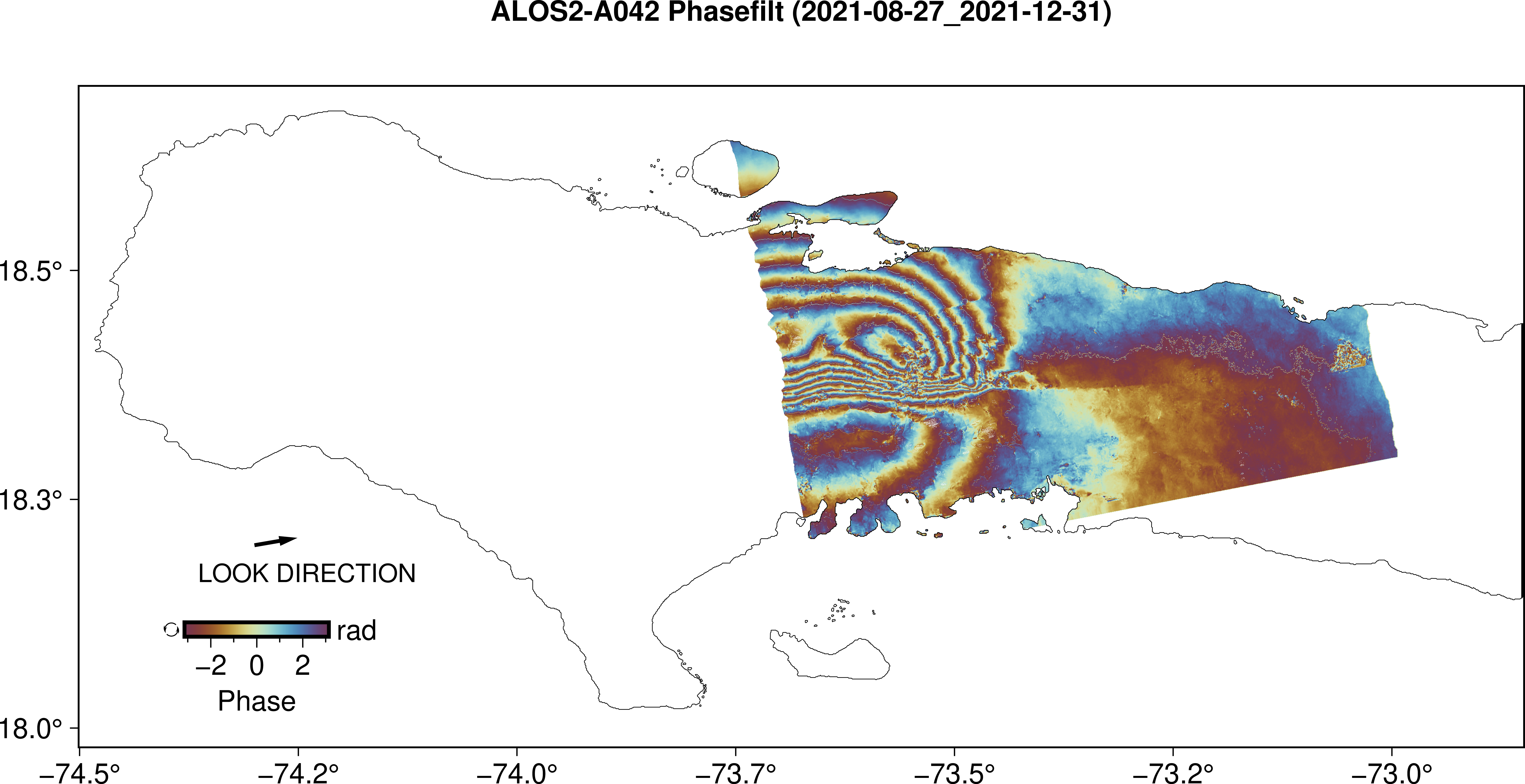
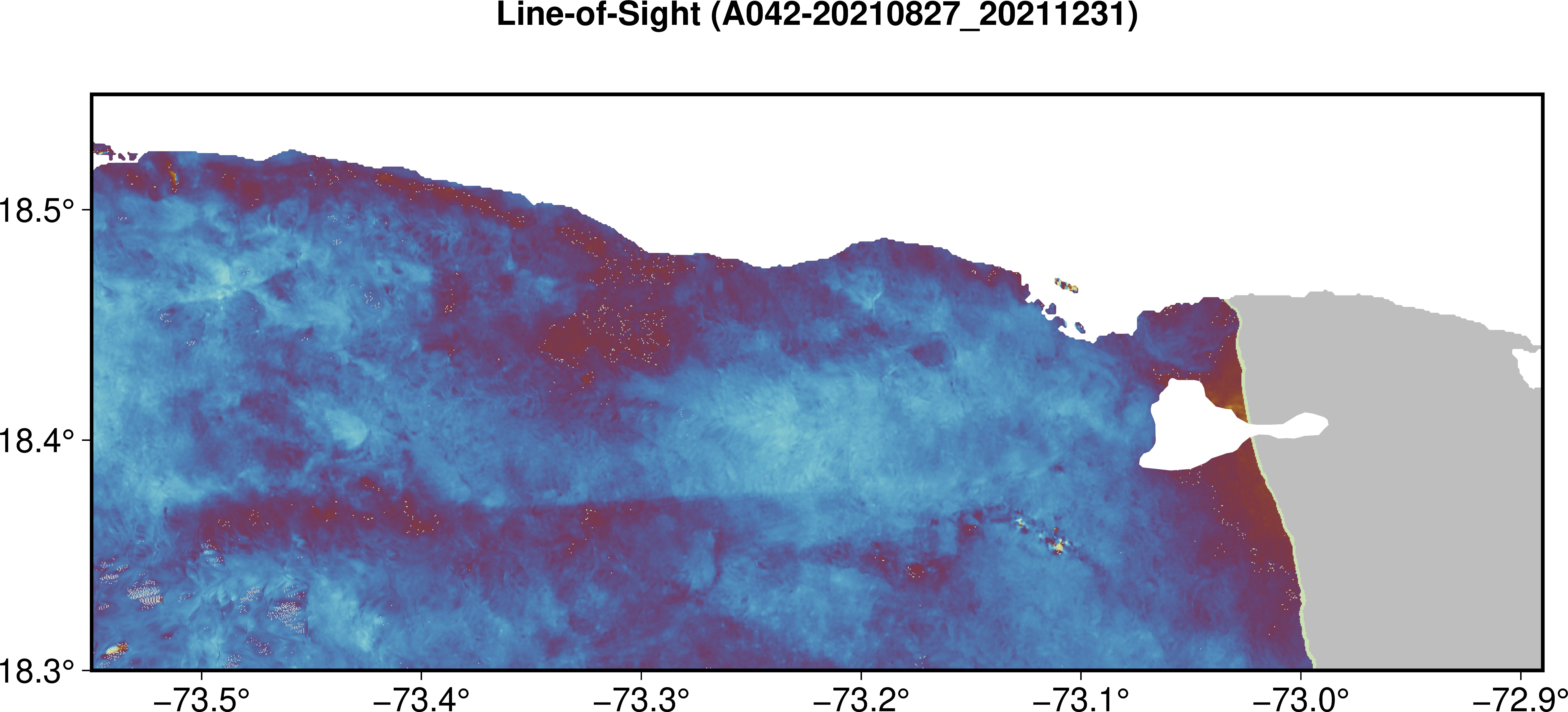
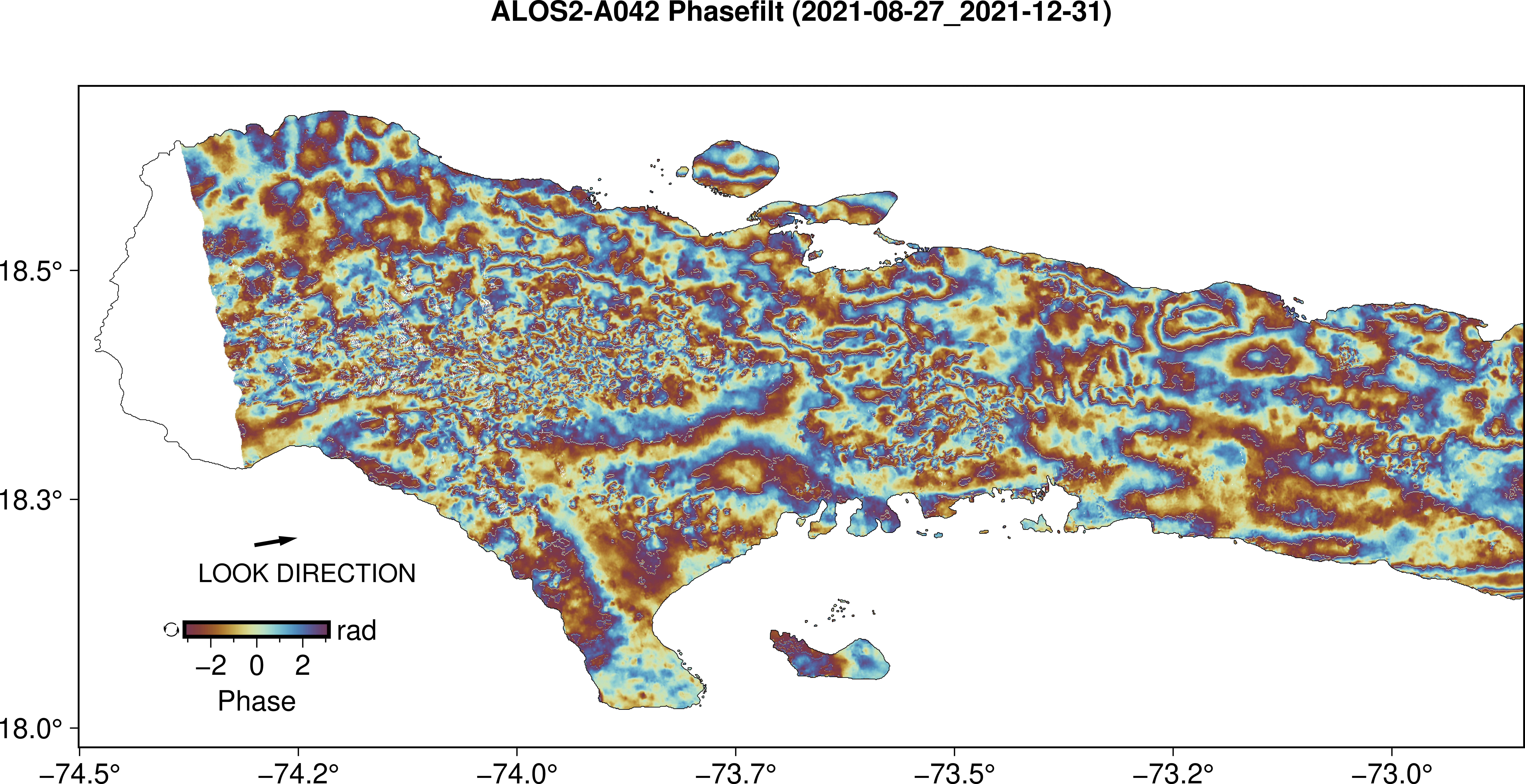
ALOS-2 Ascending Track 042 (Stripmap): Pair
2021/08/27 - 2021/12/31
Postsesismic & secondary fault structures
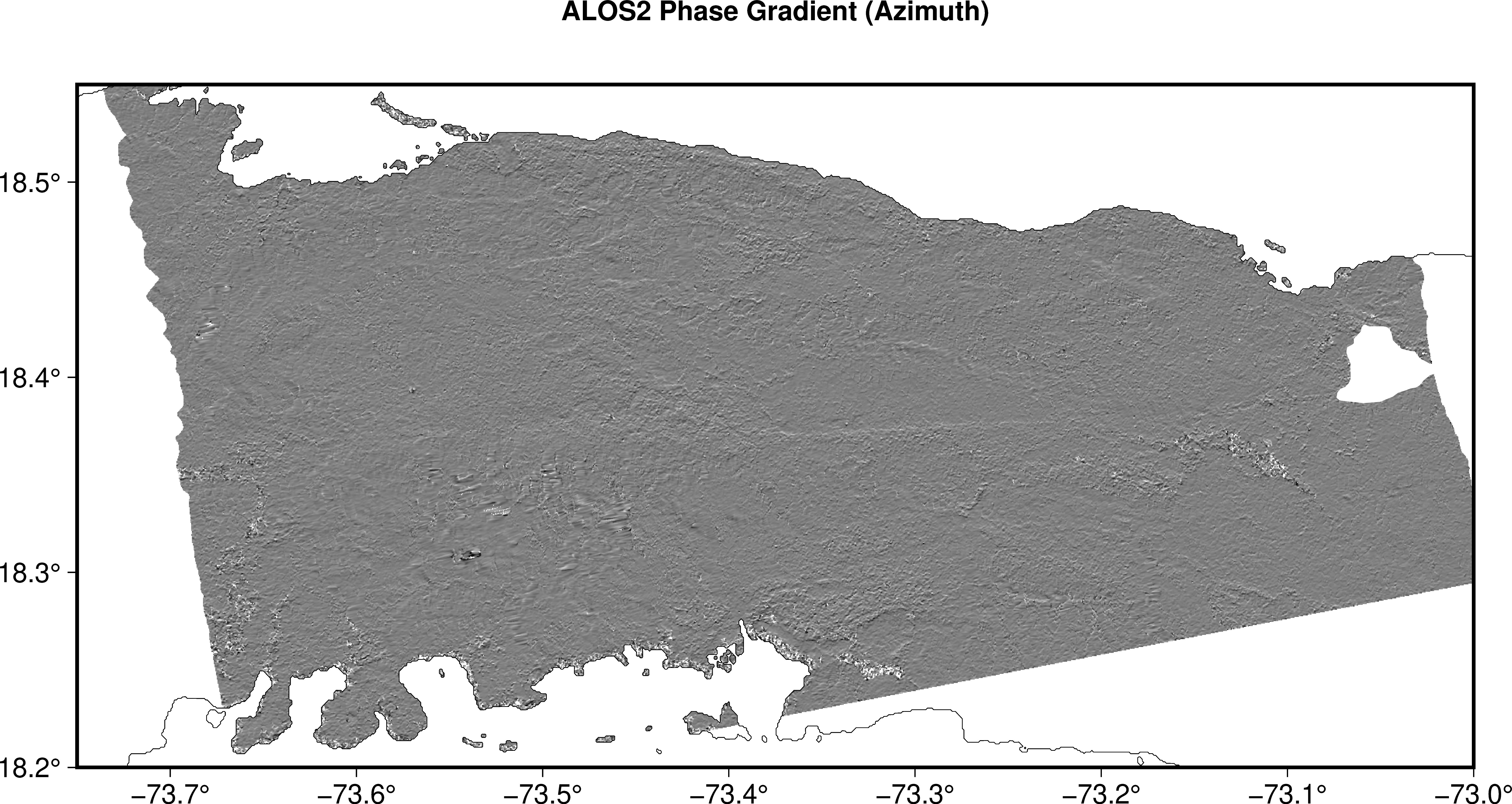
PHASE: phasefilt_ll.grd
PHASE
GRADIENT: yphase_mask_ll.grd
LINE OF
SIGHT: los_ll_dtr.grd
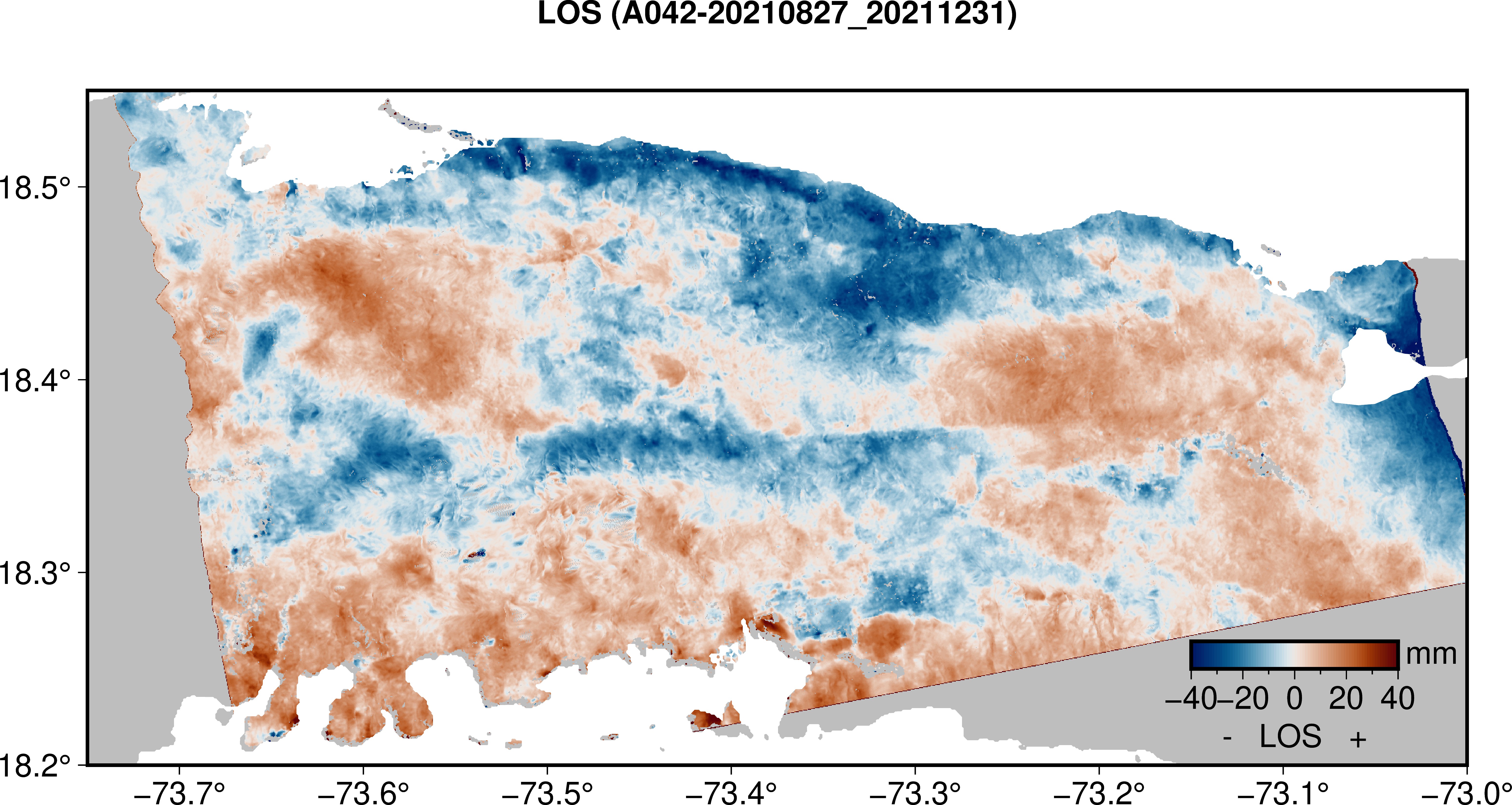
ALOS-2 Ascending Track 042 (Stripmap):
Pair 2021/01/01 -
2021/12/31
All Co & postseismic (Jan 1 - Dec
31)
PHASE: phasefilt_ll.grd
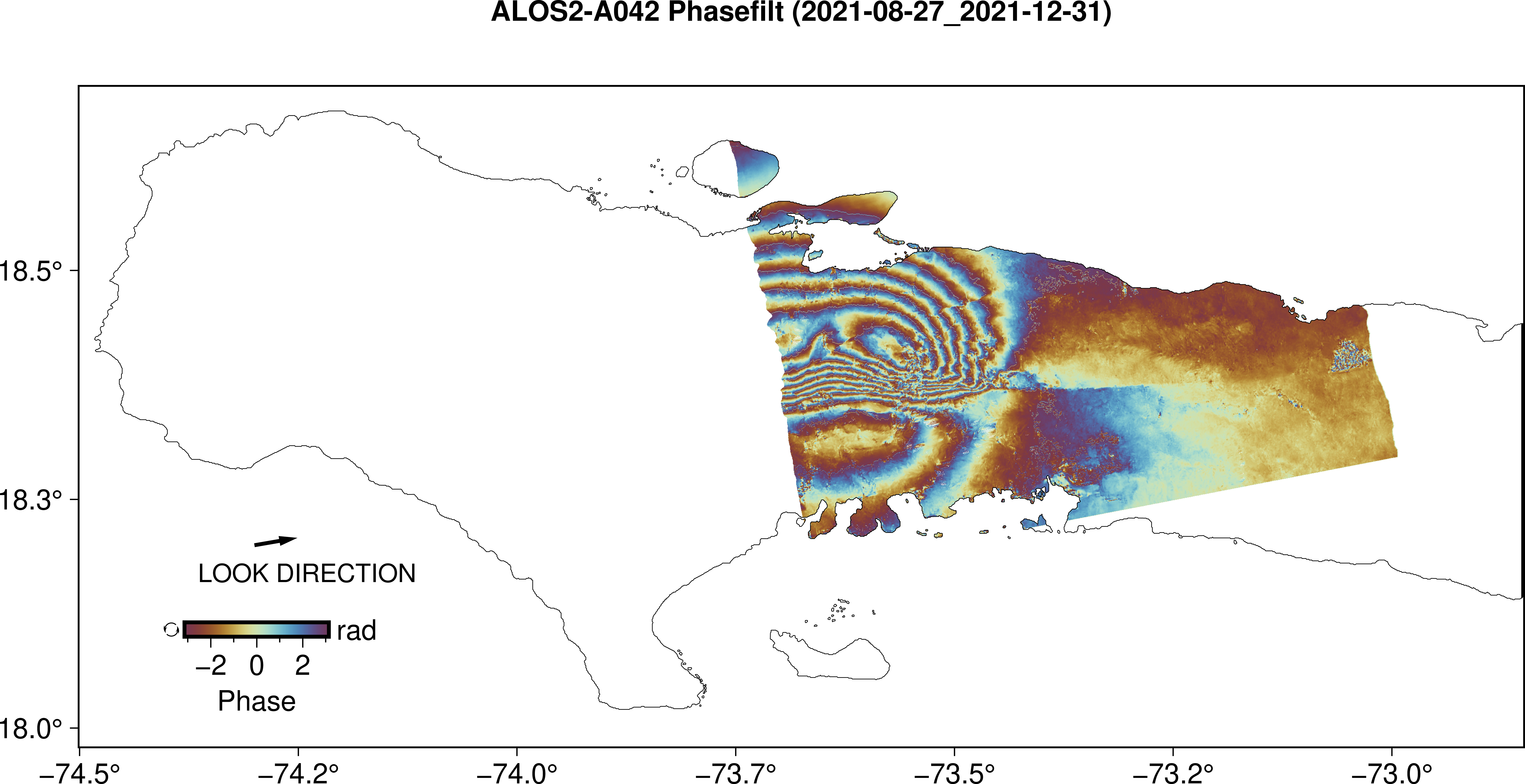
PHASE
GRADIENT: yphase_mask_ll.grd
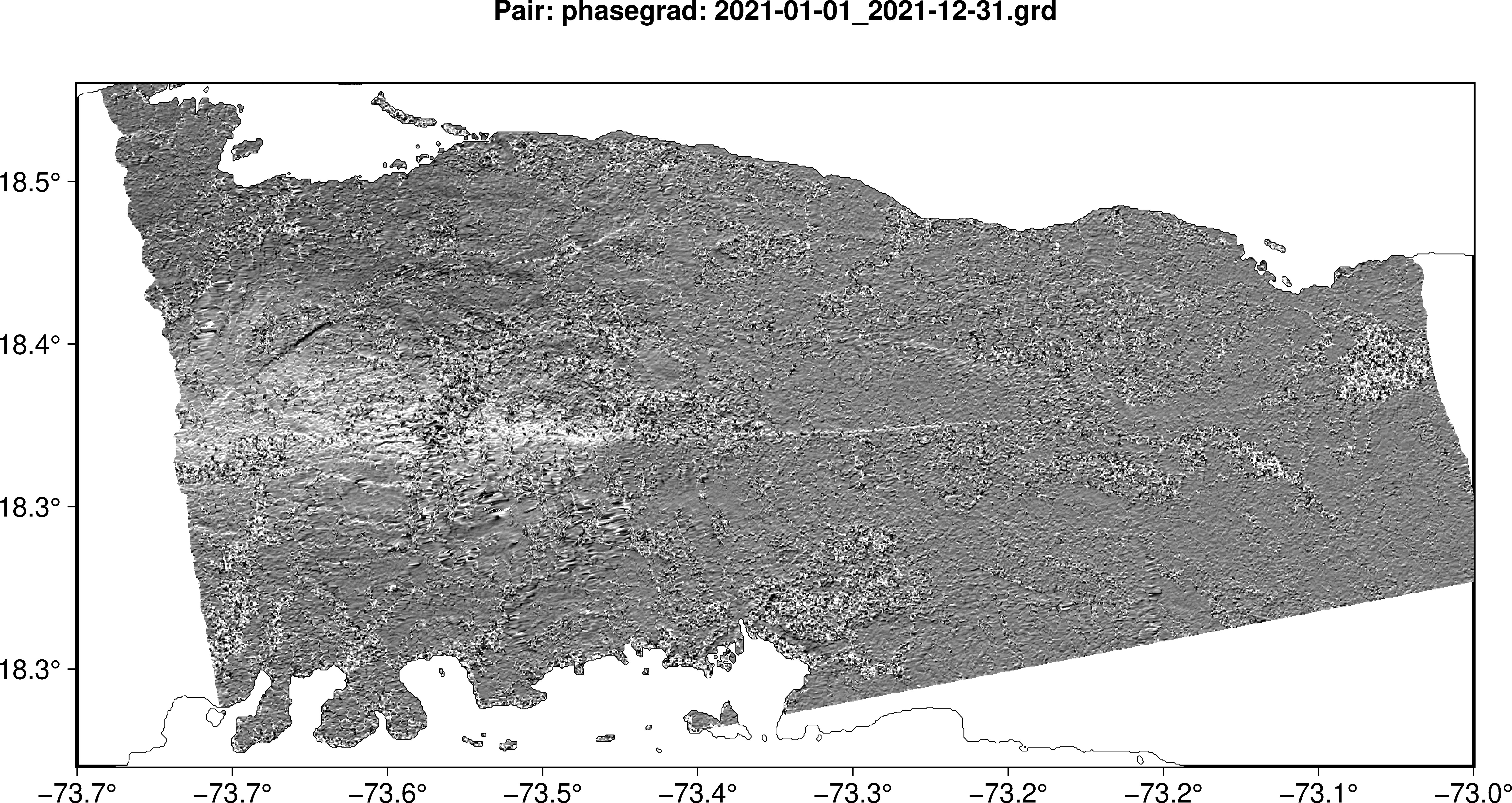
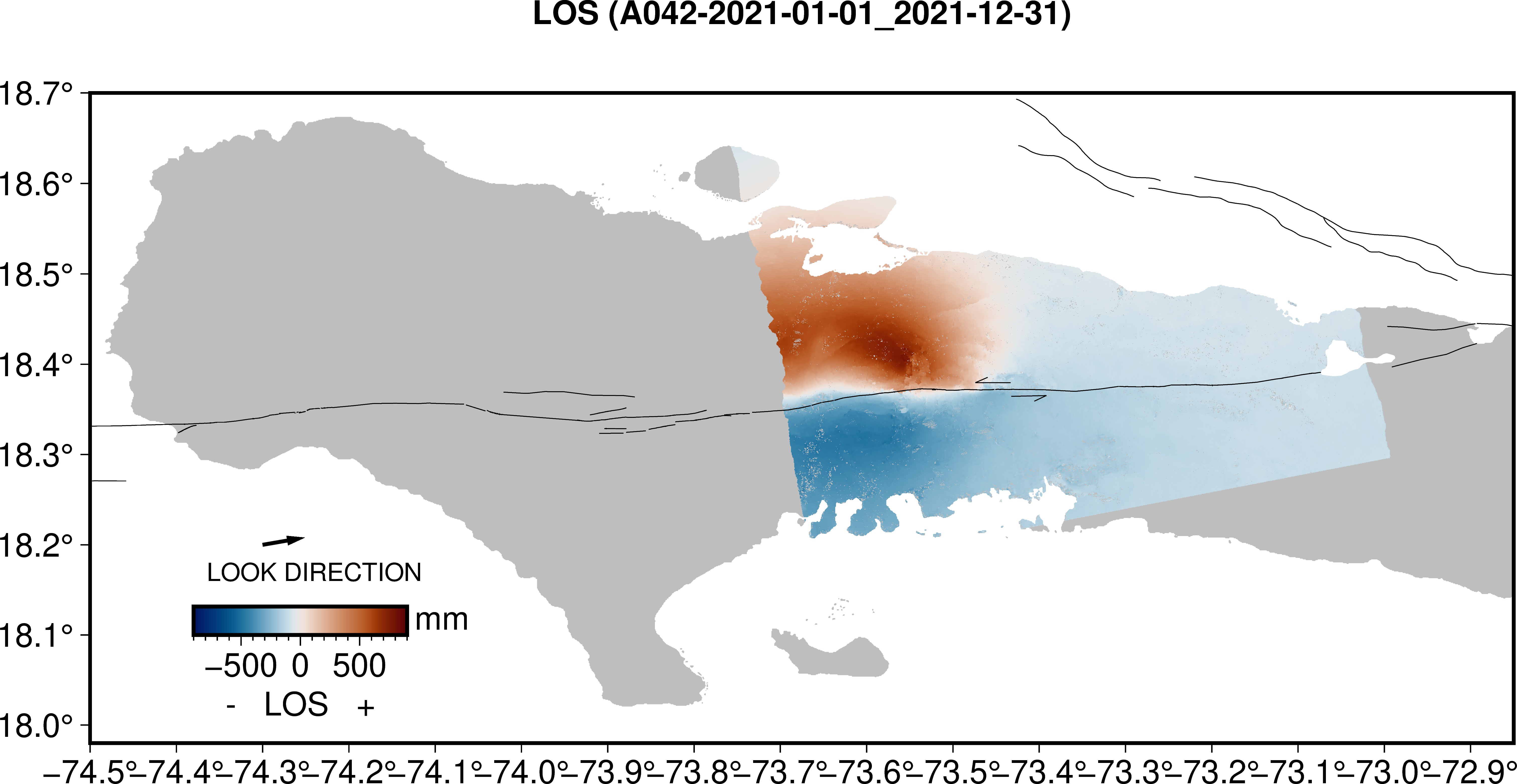
LINE
OF SIGHT:
los_ll.grd
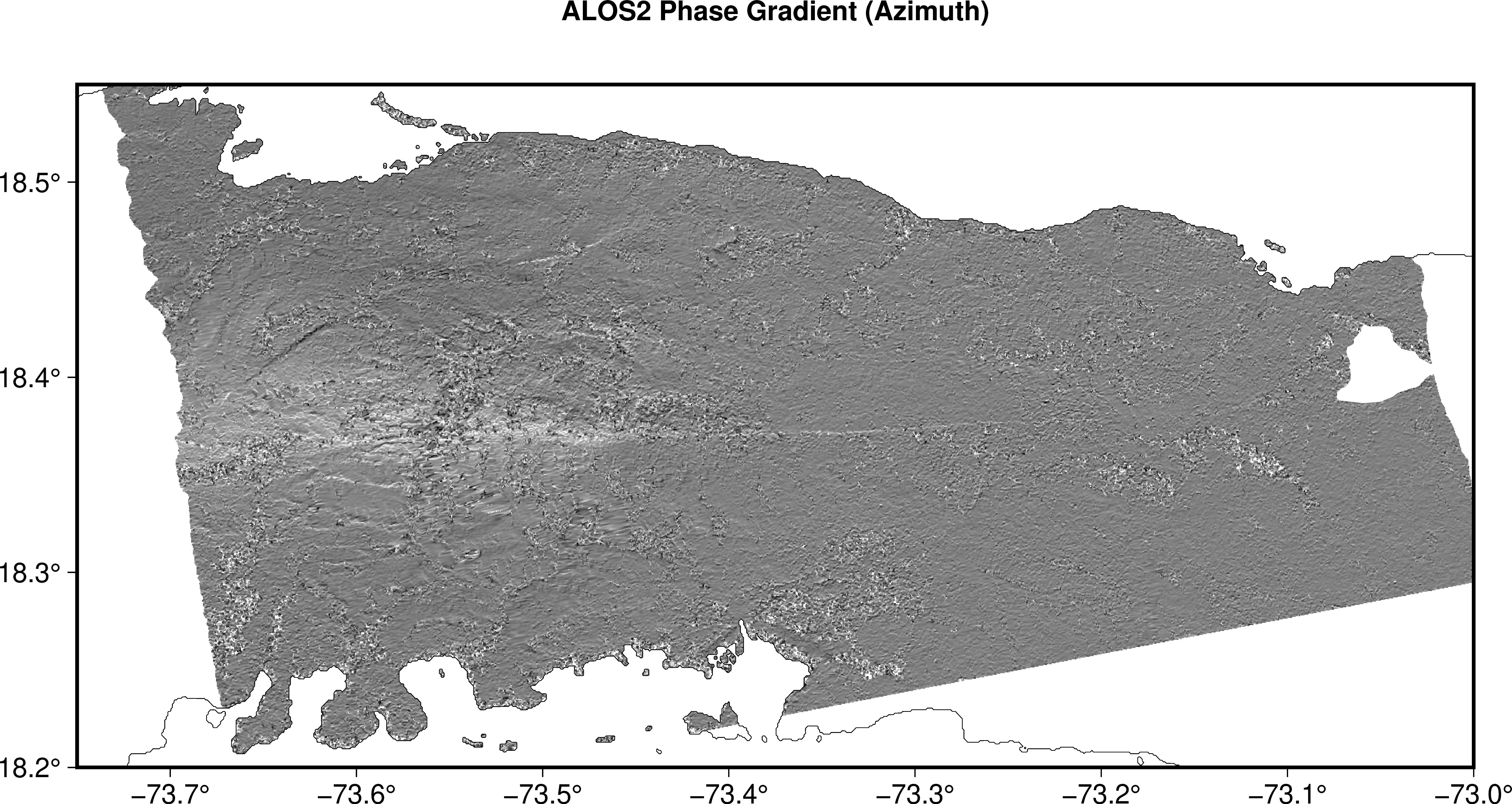
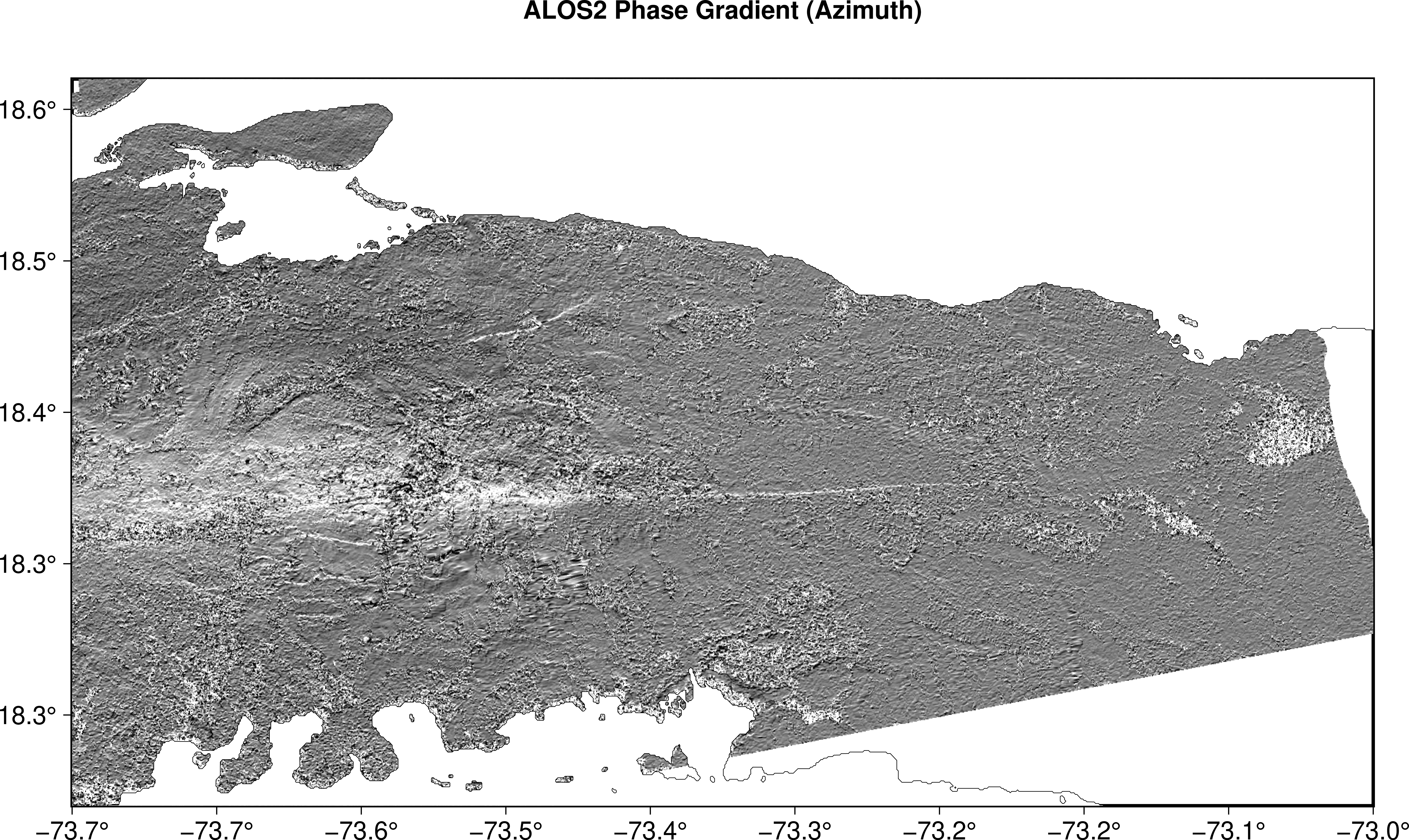
ALOS-2 Ascending Track 042 (Stripmap):
Phase gradient stack
The gradient of the phase taken
in the azimuth (flight) direction and stacked
using all ALOS-2 ascending track pairs between
Dec 23, 2020 and Dec 31, 2021 (3 pairs for A042
and 5 pairs for A043)
PHASE
GRADIENT
STACK: yphase_mask_ll_stack.grd
ALOS-2 Ascending Track 043
(Stripmap): 2020/12/23
- 2021/08/18
Coseismic
& surface rupture
PHASE:
phasefilt_ll.grd
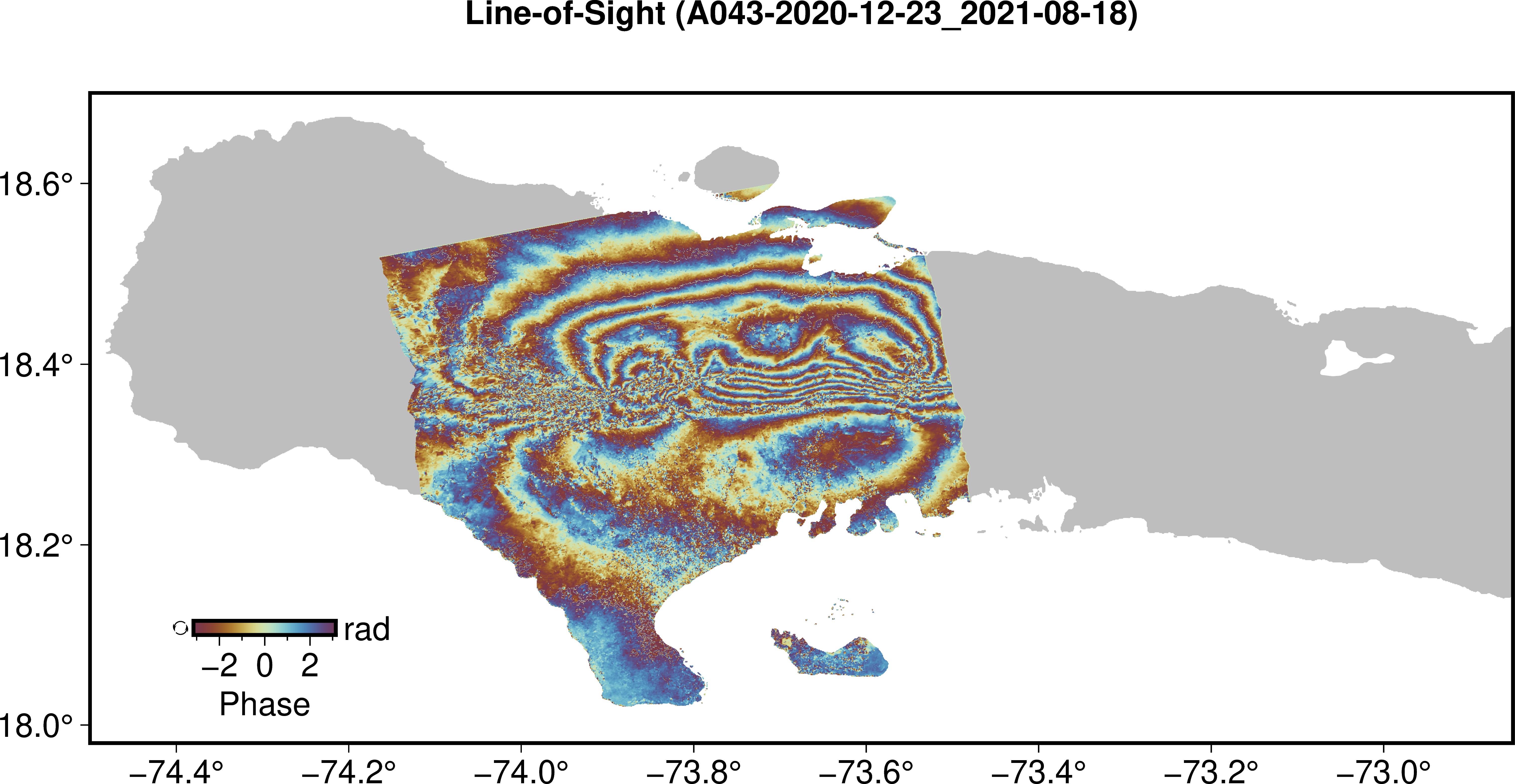
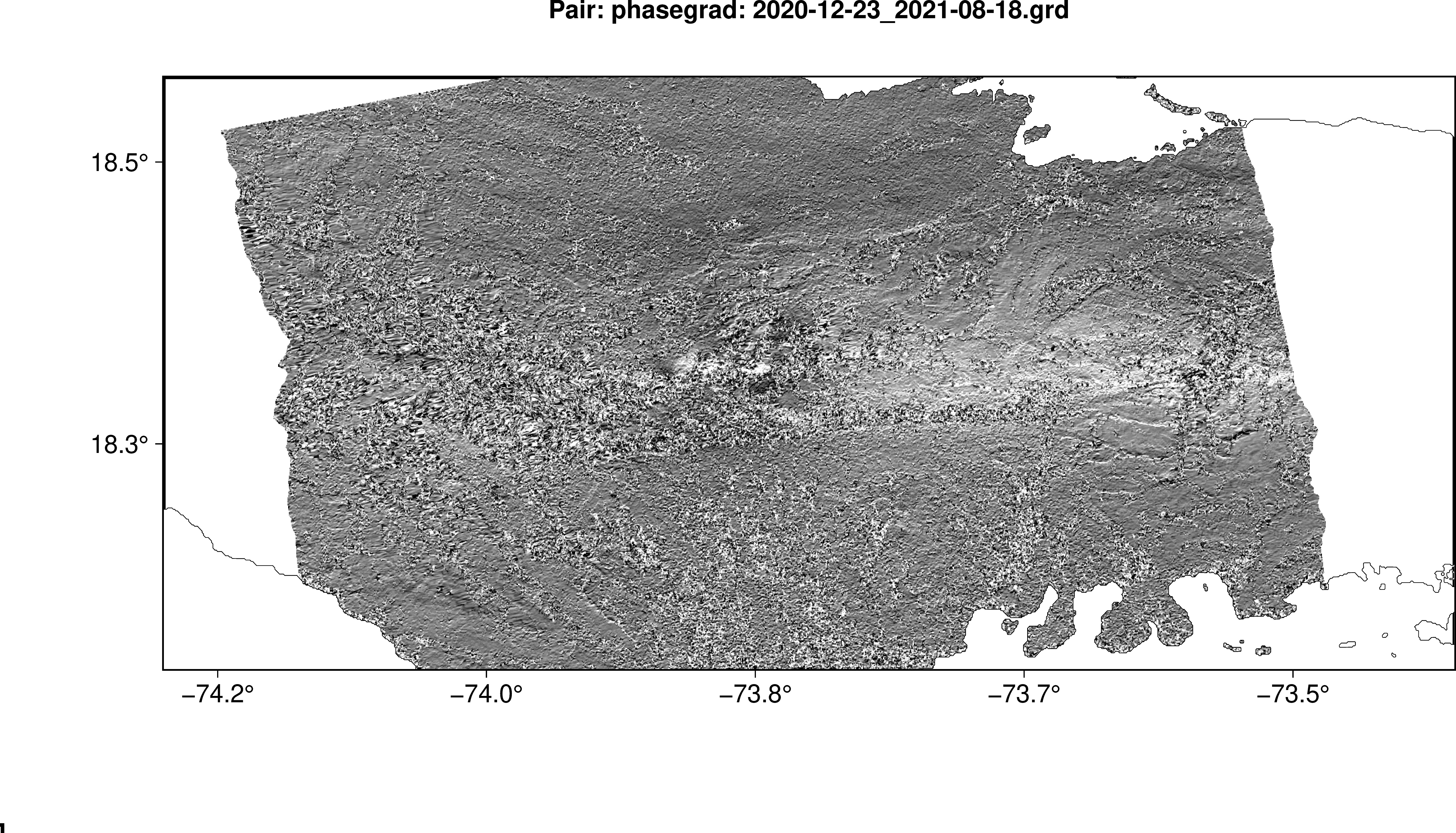
PHASE
GRADIENT: yphase_mask_ll_2020-12-23_2021-08-18.grd
LINE OF
SIGHT: los_ll.grd

ALOS-2 Ascending Track 043 (Stripmap):
Phase gradient stack
The gradient of the phase
taken in the azimuth (flight) direction and
stacked using all ALOS-2 ascending track
pairs between Dec 23, 2020 and Dec 31, 2021
(3 pairs for A042 and 5 pairs for A043)
ALOS-2 Descending Track 138
(ScanSAR): 2019/12/10
- 2021/08/17
Coseismic
Deformation.
PHASE:
phasefilt_ll.grd
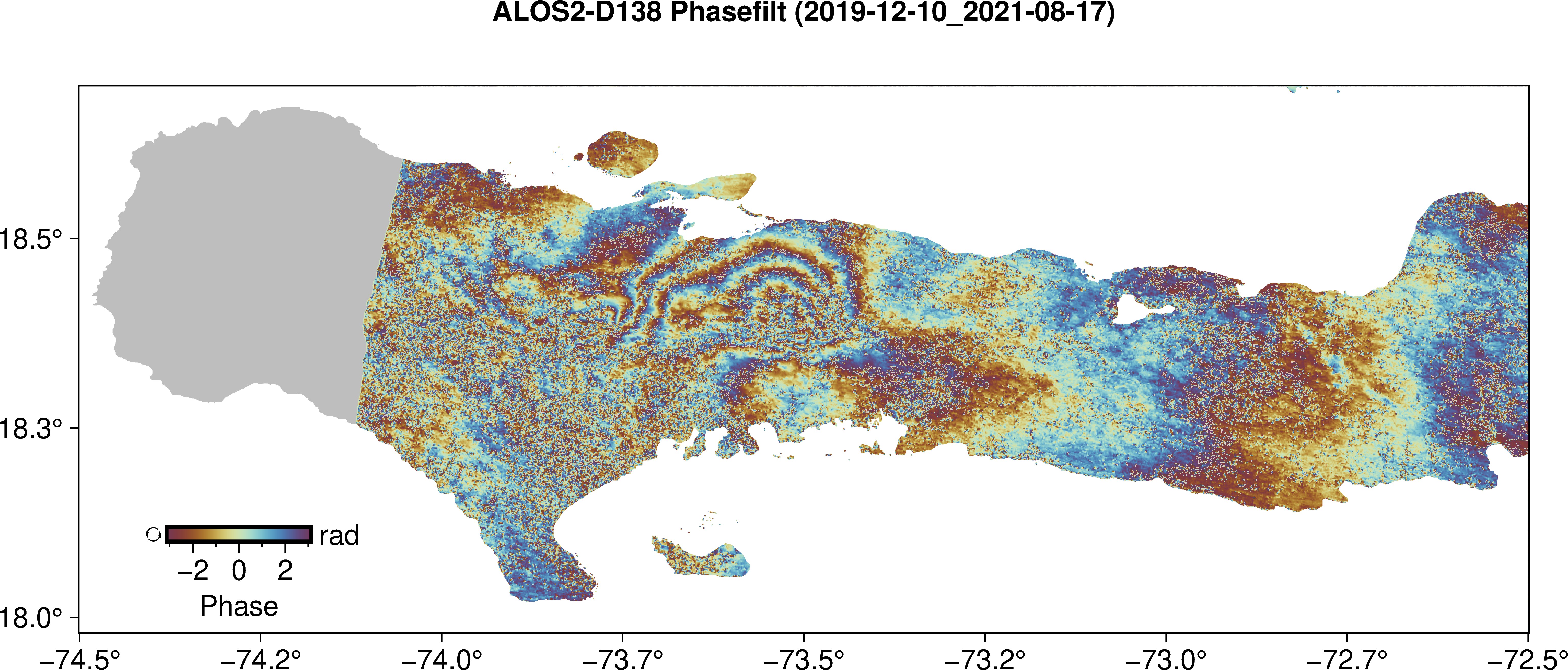
PHASE
GRADIENT: N/A
LINE
OF SIGHT:
los_ll_dtr.grd

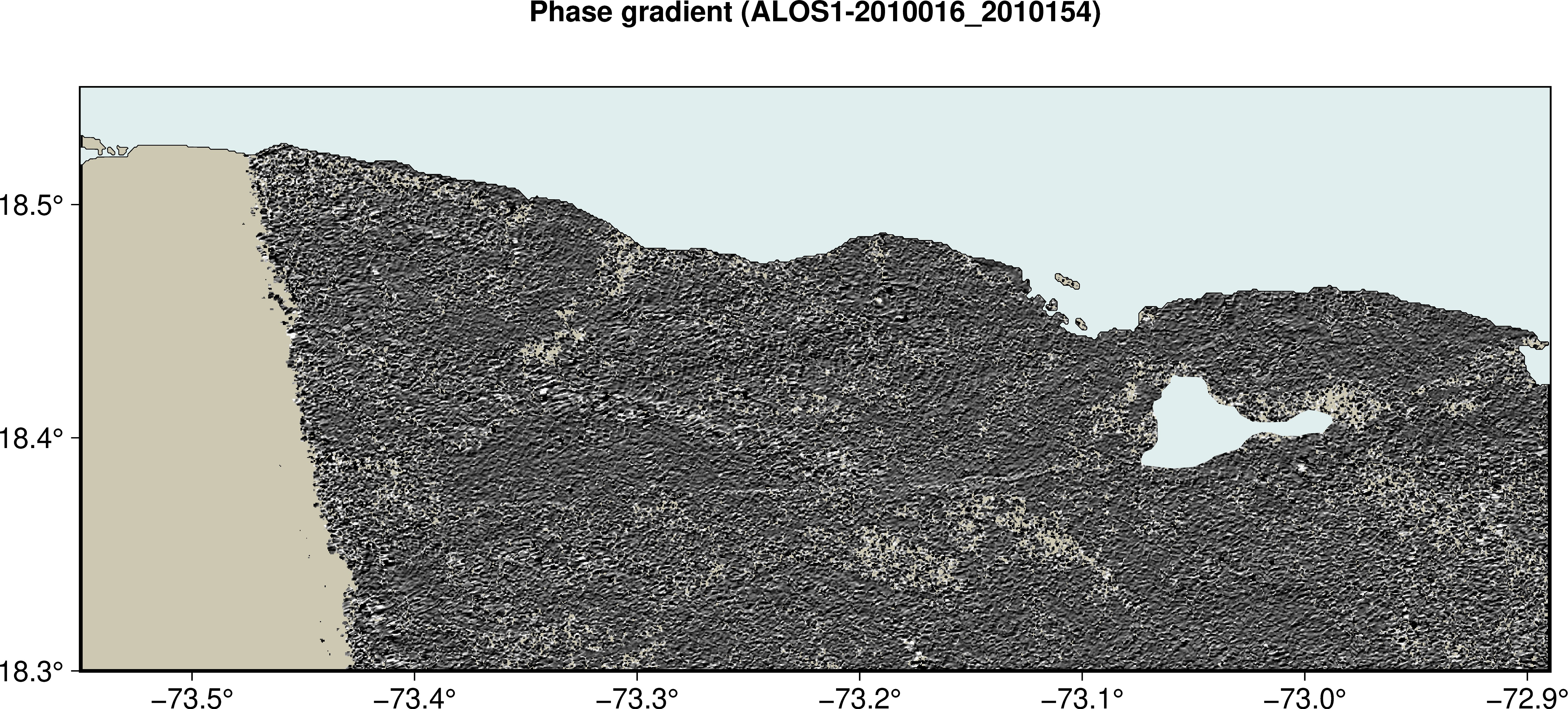
ALOS-1 Ascending Track 138
(FBD): 2010/01/16
- 2010/06/23
2010
Postseismic Deformation
PHASE: phasefilt_ll.grd
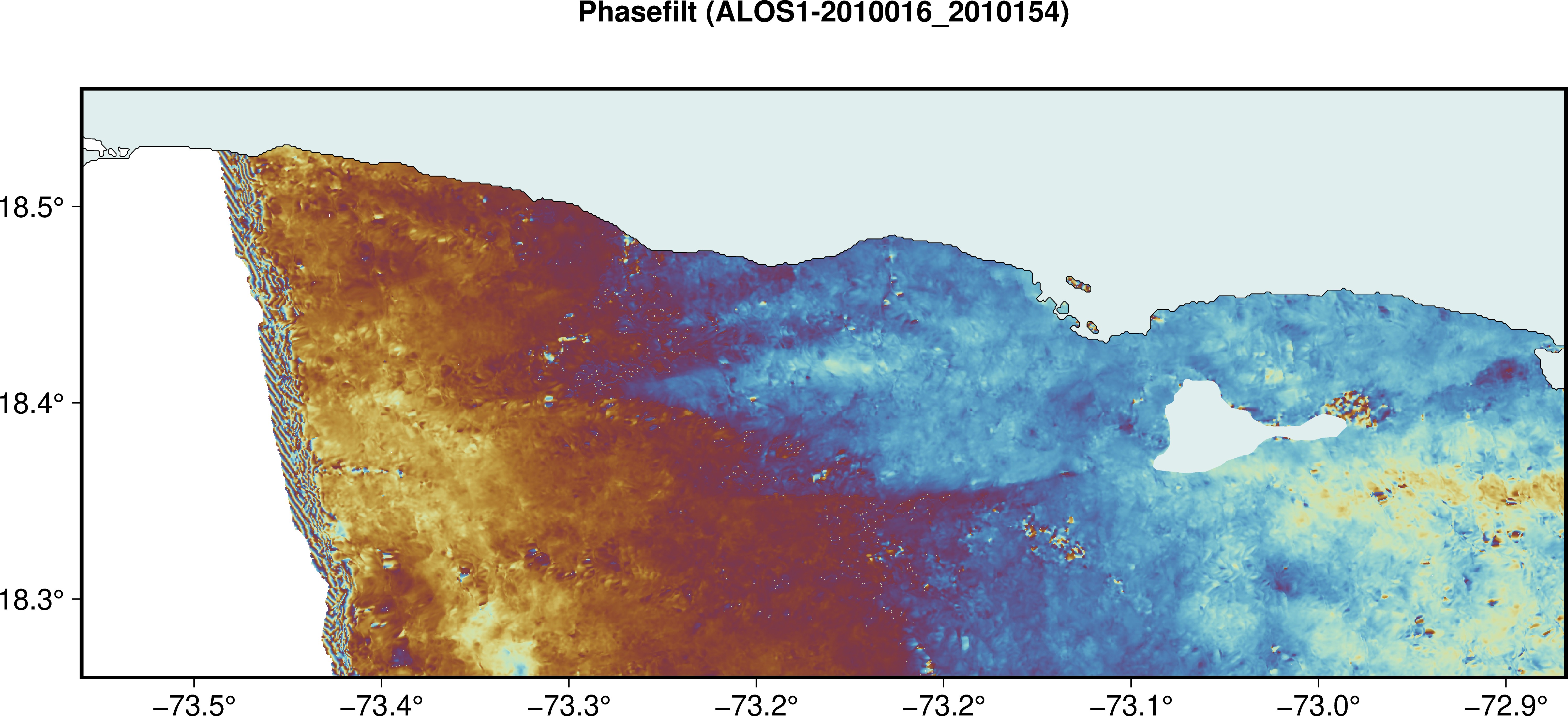
PHASE
GRADIENT: yphase_mask_ll.grd
Sentinel-1 Descending track D142:
2021/08/03 - 2021/08/15
PHASE: phasefilt_ll.grd
Sentinel-1 Descending track D142:
2021/08/15 - 2021/08/21
Post-seismic
Interferogram
Sentinel-1 Descending track
D142: 2021/08/21 - 2021/08/27
Post-seismic
Interferogram
Sentinel-1 Ascending track A004: 2021/08/05
- 2021/08/17
Sentinel-1 Ascending track
A004: 2021/08/17 - 2021/08/23
Post-seismic
Interferogram
PHASE: phasefilt_ll.grd
Sentinel-1 Ascending track
A004: 2021/08/23 - 2021/08/29
Post-seismic
Interferogram
Acknowledgements:
Rapid
InSAR data processing was
supported by a National
Science Foundation RAPID grant
(Grant #2150704). We
thank the operators of the
Ayiti-Séismes earthquake monitoring
network at Bureau des Mines, Faculté
des Sciences, Laboratoire URGéo,
Université d'état d'Haïti, Ecole
Normale Supérieur, and Laboratoire
Géoazur for making aftershock
locations free and openly available.
We thank Sylvert Paul and Francoise
Courboulex at GéoAzur, Eric Calais
at ENS, and Jeremy Maurer at
Missouri University of Science and
Technology for helpful discussions
related to the earthquake. We thank
ESA for the rapid acquisition and
distribution of Sentinel-1 data. We
thank JAXA for access to ALOS-1 and
ALOS-2 data. The development of the
GMTSAR software, and specifically
the processing chain for Sentinel-1
and ALOS-2, was supported by the
National Aeronautics and Space
Administration (NASA) and the
National Science Foundation through
the NASA Earth Surface and Interior
program (NNX16AK93G and
80NSSC19K1043), the NSF Office of
Advanced Cyberinfrastructure program
(OAC-1834807), and the NSF
EarthScope program (EAR-1147435,
EAR-1424374, EAR-1614875).